Important Components of Medical Billing Workflow
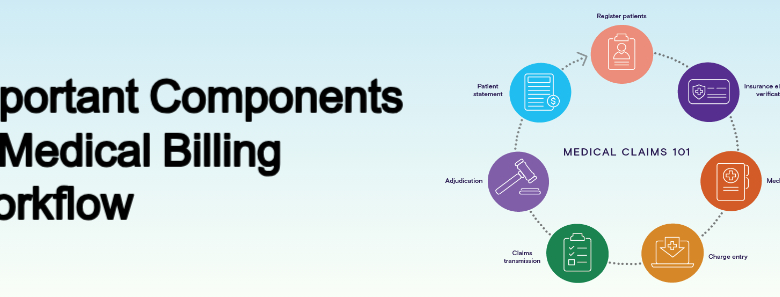
Introduction Medical billing is a critical process in the healthcare industry, ensuring that healthcare providers are reimbursed for their services. A streamlined medical billing workflow not only improves financial outcomes but also ensures compliance with regulations and enhances patient satisfaction. This article provides an updated and detailed overview of the essential components of an efficient medical billing workflow. Also Read: Role of Medical Coding and Revenue Cycle Management Patient Registration The medical billing process begins with accurate patient registration. This step involves collecting and verifying essential patient information, such as: Full name, date of birth, and contact details Insurance provider and policy details Medical history and primary care physician information Ensuring that all data is accurate and up-to-date minimizes the risk of claim denials later in the process. Insurance Verification and Eligibility Before providing services, healthcare providers must verify the patient’s insurance coverage. This involves: Checking the validity of the insurance policy Confirming coverage for specific services or procedures Identifying co-pays, deductibles, and out-of-pocket costs Timely verification prevents delays in reimbursement and ensures patients are informed about their financial responsibilities. Patient Check-In and Service Documentation During the patient’s visit, the front desk staff confirms registration details and collects any applicable co-payments. Simultaneously, the healthcare provider documents the services rendered, diagnoses, and any procedures performed. Proper documentation is crucial for accurate coding and billing. Medical Coding Medical coding translates the healthcare provider’s documentation into standardized codes used for billing. The most common coding systems include: ICD-10: International Classification of Diseases for diagnoses CPT: Current Procedural Terminology for procedures HCPCS: Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System for services and supplies Accurate coding ensures compliance and reduces the risk of claim denials. Charge Entry In this step, the medical billing team enters all relevant information into the billing system, including patient details, insurance information, and coded services.Ensuring accuracy during charge entry prevents errors that could lead to claim rejections. Claims Submission Claims are submitted electronically to insurance payers for reimbursement. Key considerations during this step include: Adhering to payer-specific guidelines Ensuring all required fields are completed Tracking submission to confirm receipt by the payer Modern billing software often integrates claim scrubbing tools to detect and correct errors before submission. Payment Posting and Reconciliation Once the insurance company processes the claim, payments are posted to the patient’s account. This step involves: Reviewing Explanation of Benefits (EOB) documents Identifying underpayments or overpayments Reconciling payments with claims to ensure accuracy Any discrepancies should be addressed promptly to avoid revenue loss. Denial Management Claims may be denied for various reasons, such as incorrect coding, missing information, or eligibility issues. Effective denial management involves: Analyzing denial reasons Correcting errors and resubmitting claims Implementing process improvements to prevent future denials Patient Billing and Collections After insurance payments are posted, any remaining balance is billed to the patient. Clear communication about payment options and deadlines helps reduce overdue accounts. Offering flexible payment plans can improve patient satisfaction and increase collections. Reporting and Analysis Regular reporting and analysis of billing data provide valuable insights into the efficiency of the workflow. Key performance indicators (KPIs) to monitor include: Claim acceptance rates Days in accounts receivable (AR) Denial rates and reasons Using this data, healthcare providers can identify bottlenecks and implement strategies to optimize the billing process. Best Practices for a Successful Medical Billing Workflow To maintain an efficient medical billing workflow, healthcare organizations should: Invest in training for billing staff to keep them updated on regulatory changes Utilize advanced billing software with features like automation and analytics Conduct regular audits to ensure compliance and identify errors Conclusion A well-structured medical billing workflow is essential for financial stability and operational efficiency in healthcare organizations. Providers can reduce errors, improve cash flow, and enhance the overall patient experience by focusing on each component and adopting best practices. Staying updated on industry trends and regulations ensures continued success in this critical aspect of healthcare administration.